The Delphi application and Arduino sketch can be. Delphi tutorial: serial comms. Bi-directional Communications. The serial monitor shows BOTH what the Arduino is SENDING and what the Arduino is RECEIVING. Beginning with Arduino, Part 7: Serial Communication. Arduino Serial Monitor. Arduino IDE provides a simple serial port monitor that. Using Visuino and Delphi Short Video Tutorial. By BoianM in Arduino. RS485 Serial Communication Between Arduino Mega and Arduino Nano With Visuino. By BoianM in. Arduino Tutorial Delphi 10.2 and Serial Port. Interface created with Delphi that you can control the serial port to Arduino turning on and off a Led, handle the LCD and receive messages towards the PC. The Delphi environment with the pascal language is still current and its use in Arduino. Delphi tutorial: serial comms. Bi-directional Communications. You will see that character appear in the stream of a's and b's appearing in the Arduino's serial. Arduino Delphi Serial. Smarmengol / Modbus-Master-Slave-for-Arduino. Serial Modbus. Of general Windows programming before taking on serial communications. Tutorials > Examples from Libraries > Software Serial > SoftwareSerialExample Software Serial Example. Arduino and Genuino boards have built in support for serial communication on pins 0 and 1, but what if you need more serial ports? MultiSerialMega - Use two of the serial ports available on the Arduino and Genuino Mega.
Tutorials in this series:
Overview
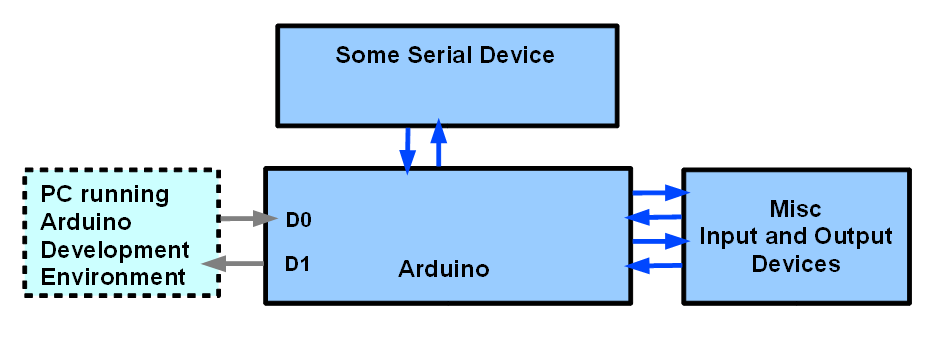
All Arduino boards have at least one built-in serial communication controller. Some boards (like the Mega) have more than one serial communication controllers. This fake makes serial communication is easy to do with these boards. Since serial communication is well documented and widely accepted, this resulting in that interfacing arduino boards to other 'smart' system very easy.
However, each serial port will consume a pair of digital pins. One for receiving, and the other one for transmitting. For example, in UNO which has one built-in serial port, pin #0 will be used for receiving (RX), and pin #1 for transmitting (TX). Therefore in projects where you use serial communication, you should avoid using these pins for other use.
Get Started
Before we can use serial port properly first we must setup correct communication settings. Complete serial communication settings would include baud rate, data bits size, stop bits size, and parity bits size. For ease of use, the last 3 have default values. If they were not specified, these default values will be used.
- 8 data bits
- 1 stop bit
- 0 (or no) parity bit

To setup these settings, we call Serial.begin function, passing the wanted settings. When we want to use 9600 bits/s baud rate and use default values for other settings, we use the following call.
Usually we only want to call this once. So setup() would be the best place to cal Serial.begin().
Writing to Serial Port
To write to a serial port, we can use one of the following functions (all of them under corresponding Serial library instance).
Use print() to send text to the receiver. For example, print(100); will send text (in ascii) '100' (without the double quotes) to the receiver instead of integer/binary value of 100.
println() acts similar with print(), except that it will automatically add carriage return and new line (line feed) characters to the end of the transmission.
write() is the most 'primitive' way to write data to your serial port, since it writes binary data to your serial port. It writes a byte or series of bytes of binary values to the serial port.
Reading from Serial Port
To read data from serial port, we could use one of these functions.
- readBytes()
However, you might need the help from the following functions in order to do better reading.
Logging Operation
To me, the most important benefit of Arduino's serial communication feature in in debugging. Except in very simple sketches, I always use serial communication to help me debug sketches. I use it to log current states/values of the running sketches. When a problem occurs, armed with the logged information I can pinpointing the source of the problem.
Our demo this time will not involve hardware manipulation. We will only create a sketch, upload the sketch to our Arduino board, and then 'talk' to the board through serial port.
Arduino Serial Monitor
Arduino IDE provides a simple serial port monitor that we can use to send and receive data to our Arduino boards through serial port. Assuming that you already load previous sketch into your Arduino IDE, compile, and upload it into your Arduino board, you can try to interact with the sketch using the serial monitor.
To open the serial monitor, click on menu Tools - Serial Monitor, or press keyboard button combination of Ctrl+Shift+M.
Serial Communication Interface
Serial monitor will be displayed and it's automatically connected to the same serial port that used by the Arduino IDE window that started it. In this example the serial monitor was connected to COM3.
Execute the Sketch
To execute the demo sketch, just load it to Arduino IDE and upload it to your Arduino board (the compilation will be done automaticall prior the actual uploading). After that open the serial monitor. Send some integer value to it by typing the value in the top edit box and press Enter key (or click the Send button).
For example, you might get something like shown below.
Arduino Delphi Serial Communication Tutorial Pdf
Edited by LuthfiHakim, 01 May 2013 - 03:14 PM.